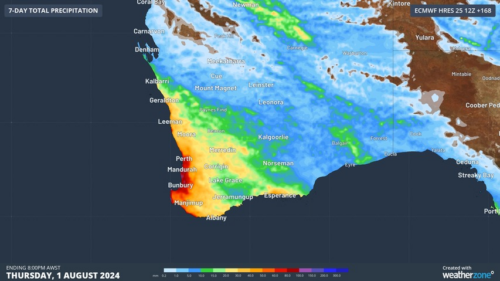
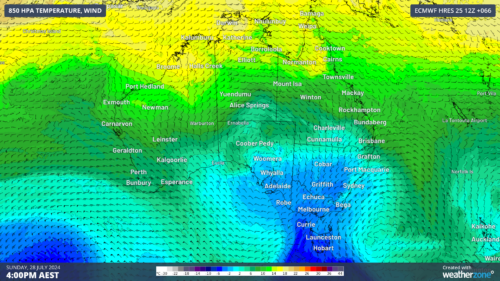
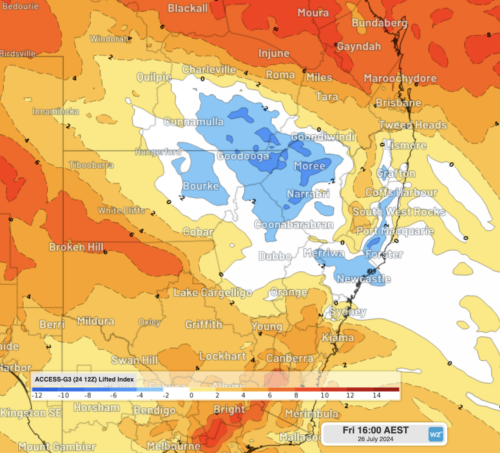
Australia has entered winter without any strong climate drivers influencing the country’s weather patterns. So, what can we expect to see across Australia during winter 2024?
The term ‘climate drivers’ refers to patterns of sea surface temperatures and associated atmospheric conditions that influence Australia’s weather on a time scale of months to seasons.
The main climate drivers that affect Australia during winter are the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO), the Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) and the Southern Annular Mode (SAM).
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is currently in a neutral ENSO state, meaning neither El Niño nor La Niña is occurring. This neutral pattern is expected to persist through the first half of winter and may last all season. However, some forecast models suggest that a La Niña episode could develop later this winter or spring.
If the ENSO remains neutral this season, this climate driver won’t have any strong influence in Australia’s weather during winter.
However, if a La Niña develops, this would promote above average rain, below average daytime temperatures and warmer nights over large areas of Australia this season.
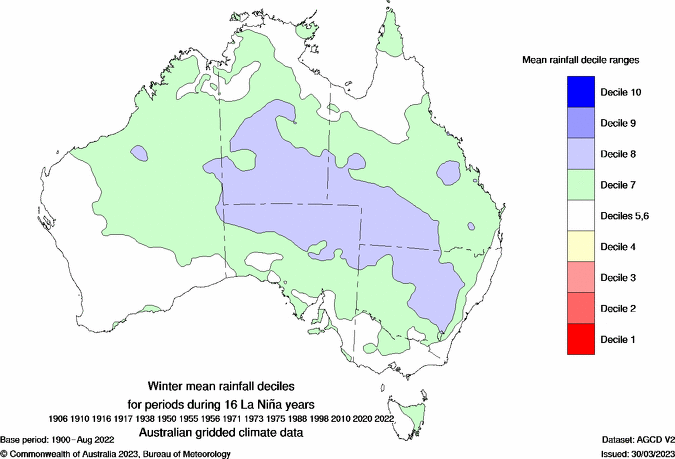
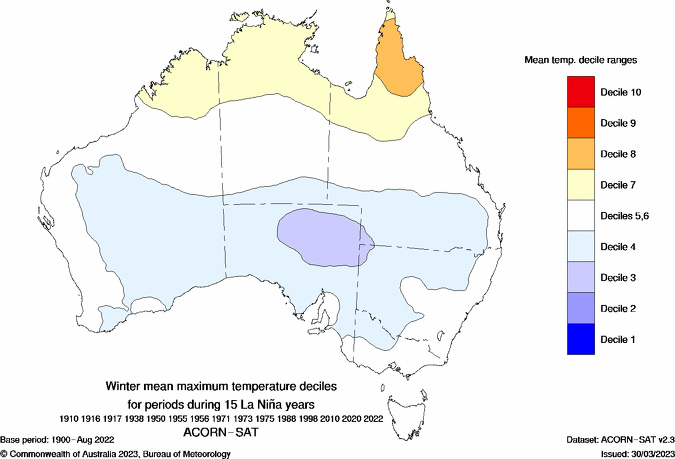
Images: Typical rainfall and maximum temperature deciles during La Niña winters in Australia. Source: Bureau of Meteorology
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean Dipole is currently neutral. Forecast models predict that it will remain neutral or trend positive in the coming months.
Like ENSO, a neutral IOD would have little influence on Australia’s weather but if a positive IOD emerges, this would shift the odds towards drier than average weather in large areas of Australia during winter. A positive IOD typically doesn’t have much influence on temperatures in Australia in winter.
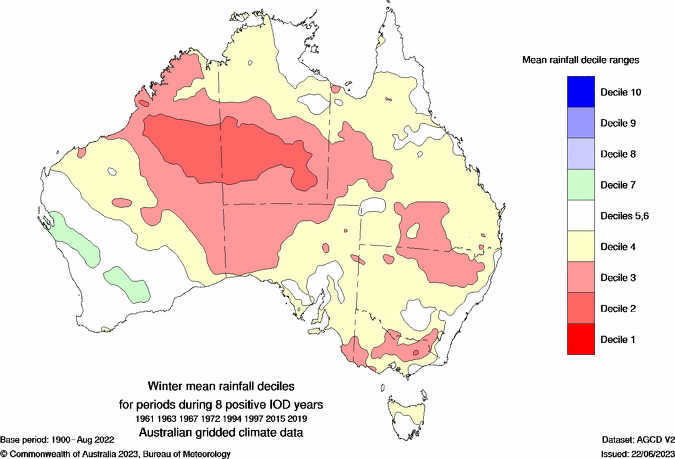
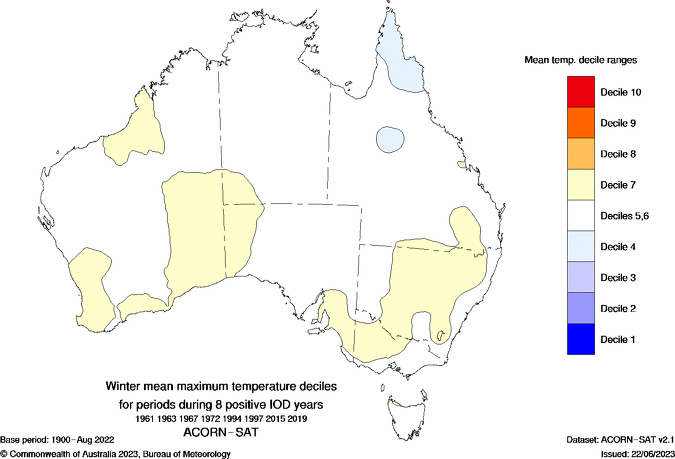
Images: Typical rainfall and maximum temperature deciles during La Niña winters in Australia. Source: Bureau of Meteorology
Southern Ocean
The Southern Annular Mode (SAM) has been weakly negative in the opening week of winter, although it is expected to trend towards more neutral or positive phases this season, particularly if a La Niña develops.
A neutral SAM typically means near-average weather in southern Australia, while a positive SAM during winter would reduce rain and snow in parts of southern Australia and increase the likelihood of rainfall in the east.
Rainfall this winter
With Australia’s main climate drivers are expected to be in either neutral or weak phases this season, there are no strong indications of above or below average rainfall this winter.
If we do continue to see a La Niña pattern developing in the Pacific Ocean and positive phases of the SAM, we could see above-average rain over parts of eastern Australia and below average rain and snow in the nation’s south.
Seasonal rainfall outlooks from the ECMWF-SEAS5 models are hinting at this pattern, predicting near-average rainfall for most of Australia, with potential for above average rain in the east and drier-than average weather in parts of the south.
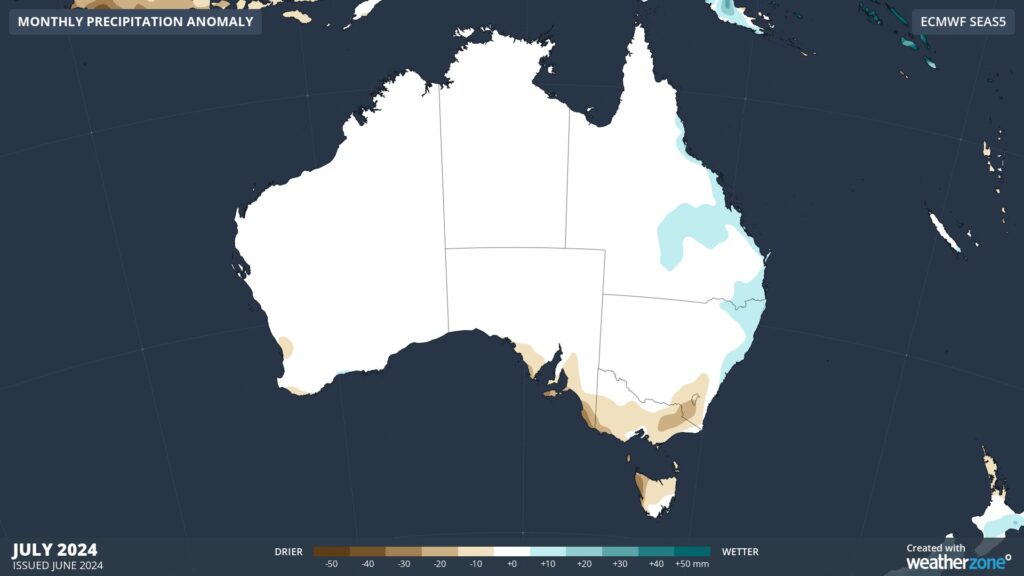
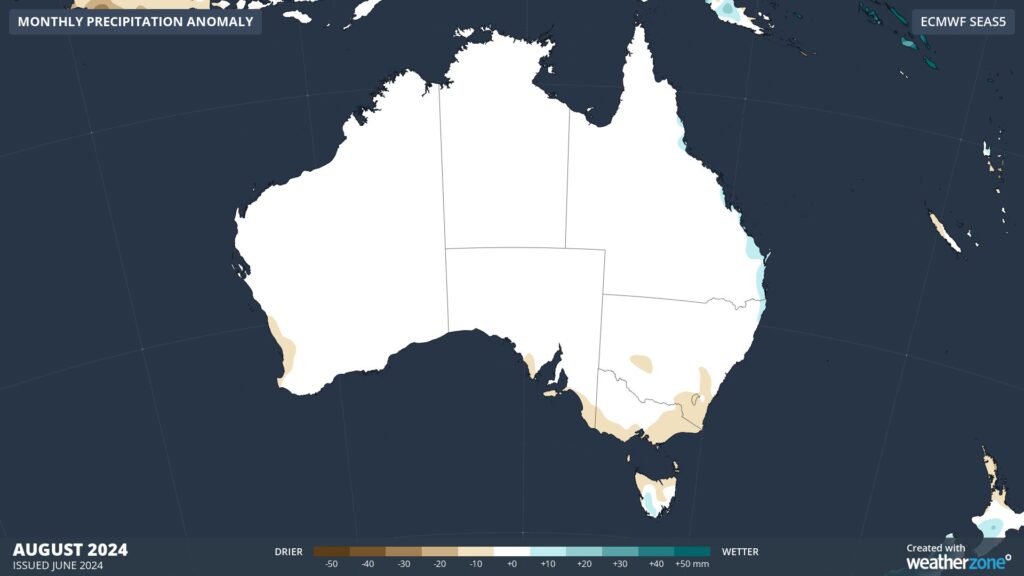
Images: Rainfall outlooks for July (top) and August (bottom) 2024.
Below-average rain in southeastern Australia may also mean below-average snow in the alpine areas, especially if this coincides with above-average temperatures.
Temperature this winter
Australia’s average temperatures in every season are influenced by the background signal of climate change, which makes it more likely than not that we will see warmer-than-average conditions compared to the past climate.
Aside from this background influence, there are no strong indications that climate drivers will push temperatures too far above or below average this season.
Without a substantial cooling influence from climate drivers, temperature outlooks are predicting warmer-than-average conditions during both day and night across most of Australia this winter.
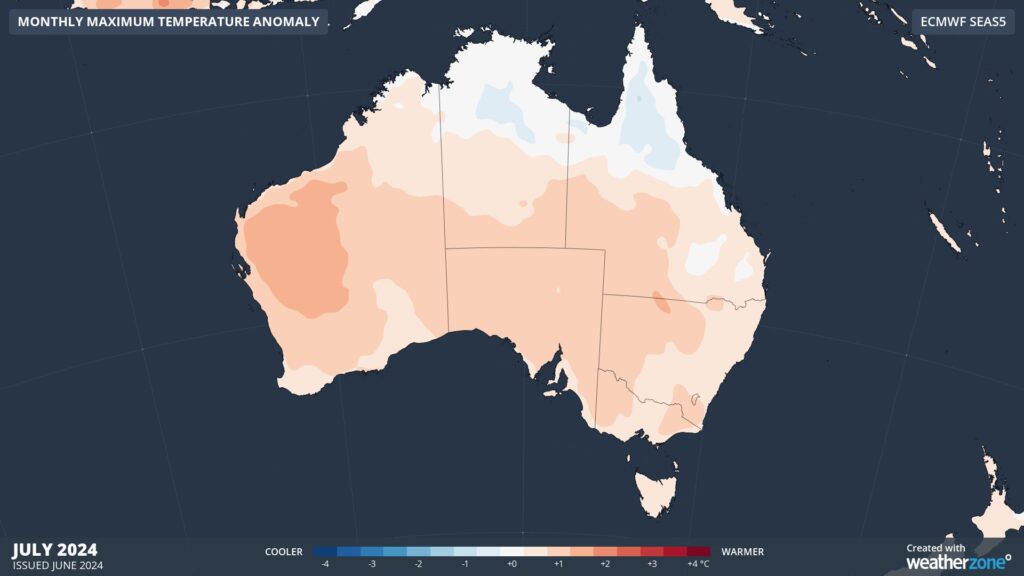
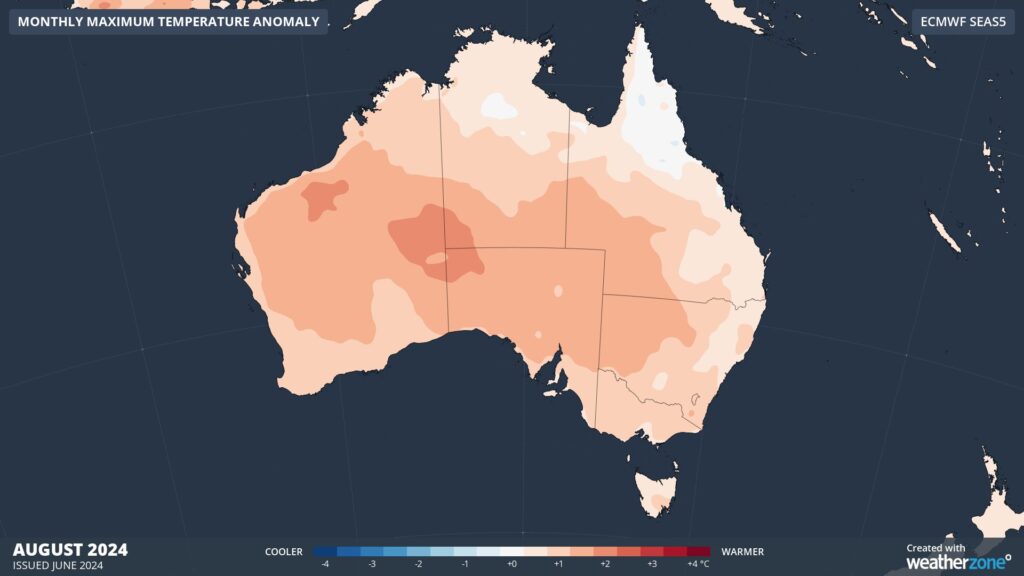
Images: Maximum temperature outlooks for July (top) and August (bottom) 2024.
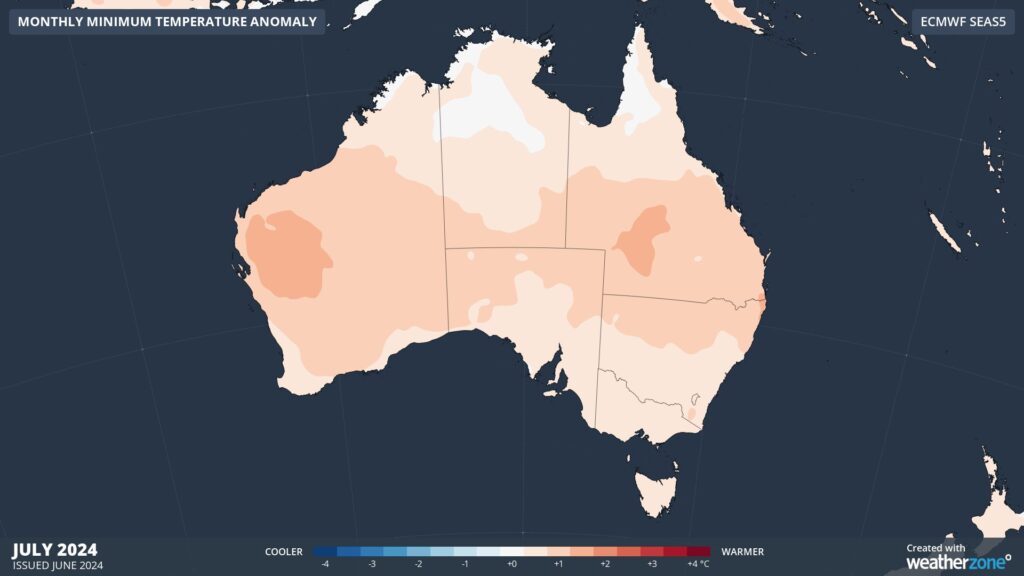
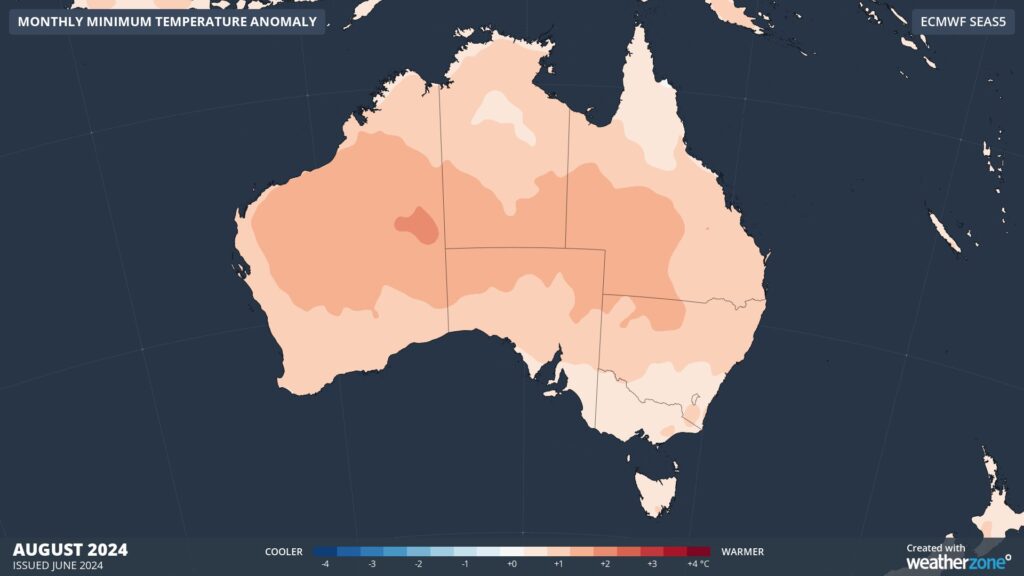
Images: Minimum temperature outlooks for July (top) and August (bottom) 2024.