La Niña is a natural phenomenon that has a significant impact on weather and climate all over the world. So let’s find out what La Niña is and how it affects the weather in Australia.
What is La Nina?
La Niña is a broad-scale circulation in the Pacific Ocean that is characterised by warmer-than-average sea surface temperatures to the northeast of Australia and abnormally cool water in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean.
The warm oceans and humid atmosphere that are associated with La Niña typically cause increased convection over the western side of the tropical Pacific Ocean. This in turn drives above average rainfall and cloud cover across much of Australia.
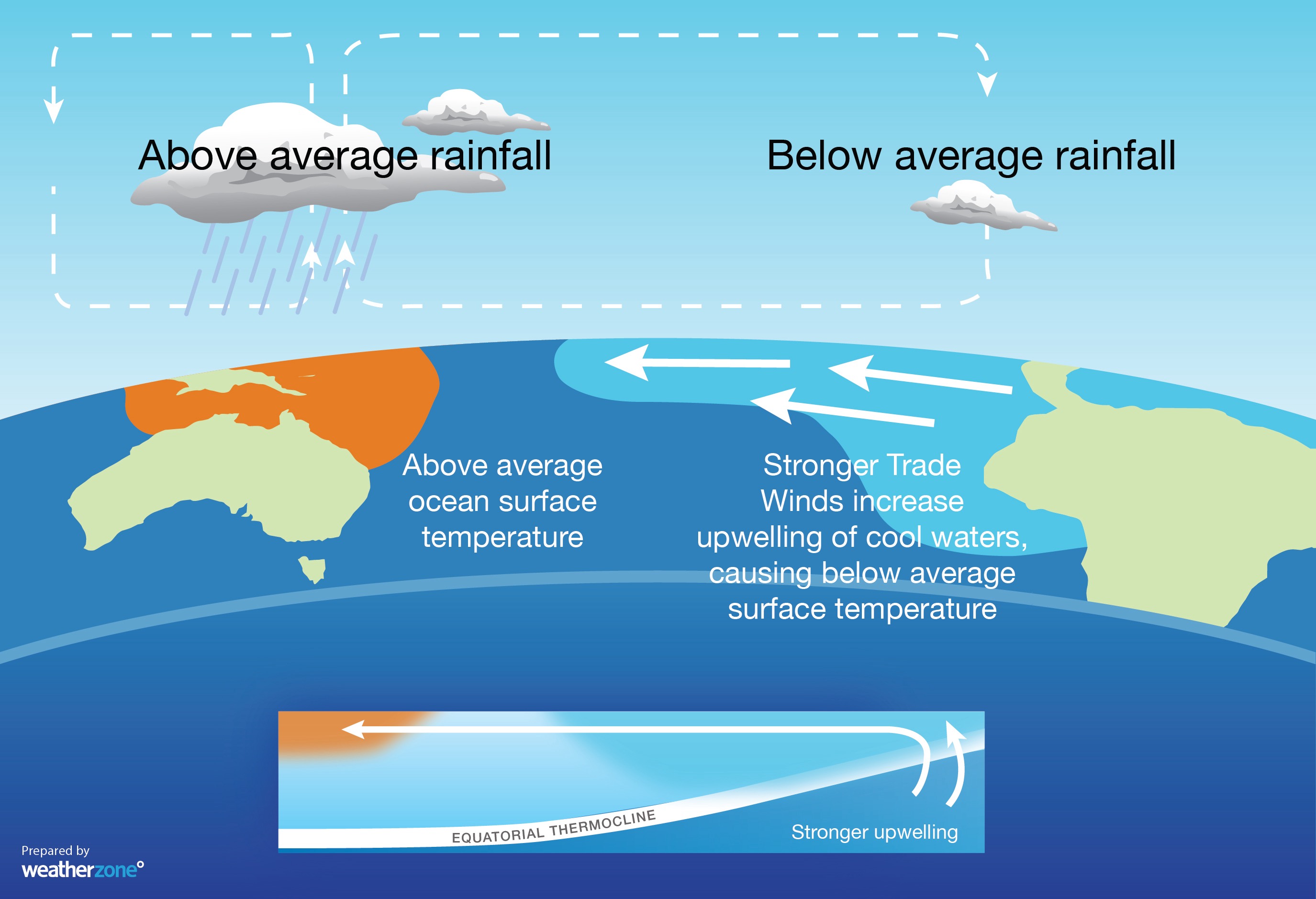
Image: Typical oceanic and atmospheric changes observed during La Niña.
La Niña is one of three phases of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation, with the other two phases being El Niño and neutral (neither La Niña nor El Niño).
La Niña events typically begin and end around the Southern Hemisphere’s autumn and have the greatest impact on Australia’s weather between winter and early-summer.
On average, La Niña occurs roughly once or twice per decade, with around half of La Niña events occurring back-to-back over consecutive years. It is rare to see three consecutive La Niña events – this has only happened three times since 1950 (1973 to 1976 and 1998 to 2001).
What causes La Niña?
La Niña is known as a coupled ocean-atmosphere phenomenon, which means that once it is underway, the ocean and atmosphere reinforce each other. As a result, and unlike some other climate drivers that affect Australia, La Niña typically persists across several consecutive seasons.
La Niña occurs when the temperature contrast that develops across the equatorial Pacific Ocean supports stronger trade winds blowing from east to west across surface of the Pacific.
These enhanced trade winds cause warmer-than-average water to pile up on the western side of the equatorial Pacific Ocean and cooler-than-average water to form in the central and western equatorial Pacific.
These pools of abnormally warm and cool water help air rise over the western Pacific Ocean and sink on the eastern side of the Pacific basin. This rising and sinking air causes enhanced convection and cloudiness near Australia, and reduced cloudiness over the central eastern Pacific Ocean.
What are the effects of La Niña?
The warm oceans and humid atmosphere that are associated with La Niña typically drive above average rainfall and cloud cover across much of Australia, especially between winter and early summer.
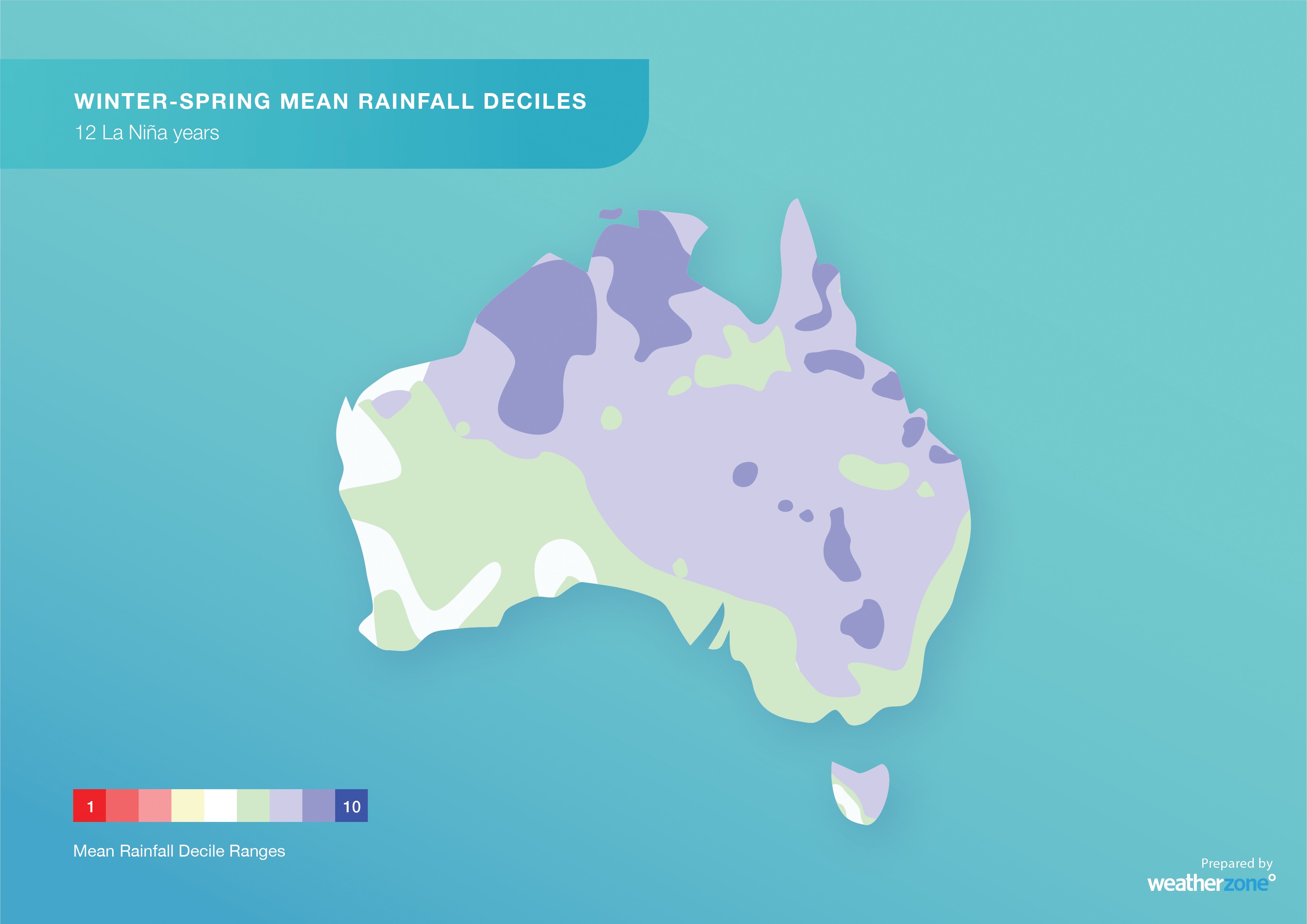
Image: Observed rainfall deciles during 12 past La Niña winter-spring periods combined, showing that large areas of Australia typically experience above-average rain during La Niña.
The increased cloud cover and rainfall during La Niña also promotes cooler-than-average daytime temperatures across Australia, but warmer than average night-time temperatures.
Heat extremes are generally less frequent during La Niña years, while prolonged spells of lower-intensity heat are generally more common.
The warm oceans near northern Australia make La Niña favourable for tropical cyclone development. La Niña also increases the likelihood of an earlier-than-usual start to the cyclone season and Australia’s northern wet season.
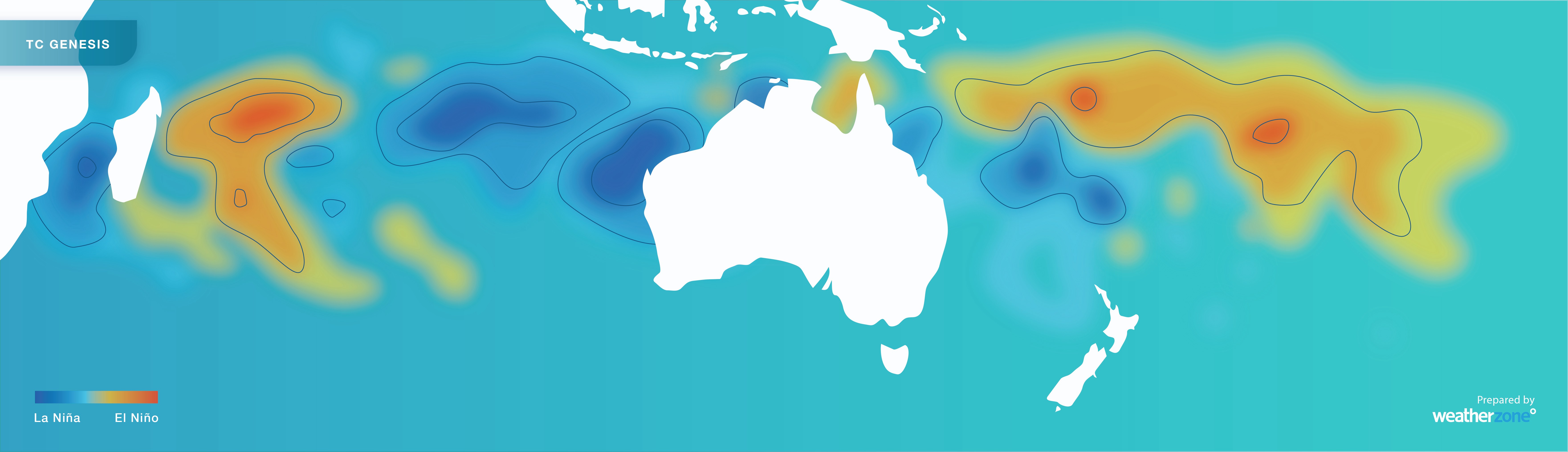
Image: Influence of La Niña and El Niño on tropical cyclone formation near Australia. Blue shading shows where tropical cyclones are more likely to occur during La Niña.
During La Niña years, the Southern Annular Mode (SAM) usually remains in a predominantly positive phase. This typically promotes rainfall in eastern Australia, while reducing the frequency of strong wind and thunderstorm events in the south and east.
The broad-scale influence of La Niña on the ocean and atmosphere affects weather patterns around the world. For example, while rainfall typically increases over Australia during La Niña, parts of North America often experience more bushfires and drought.
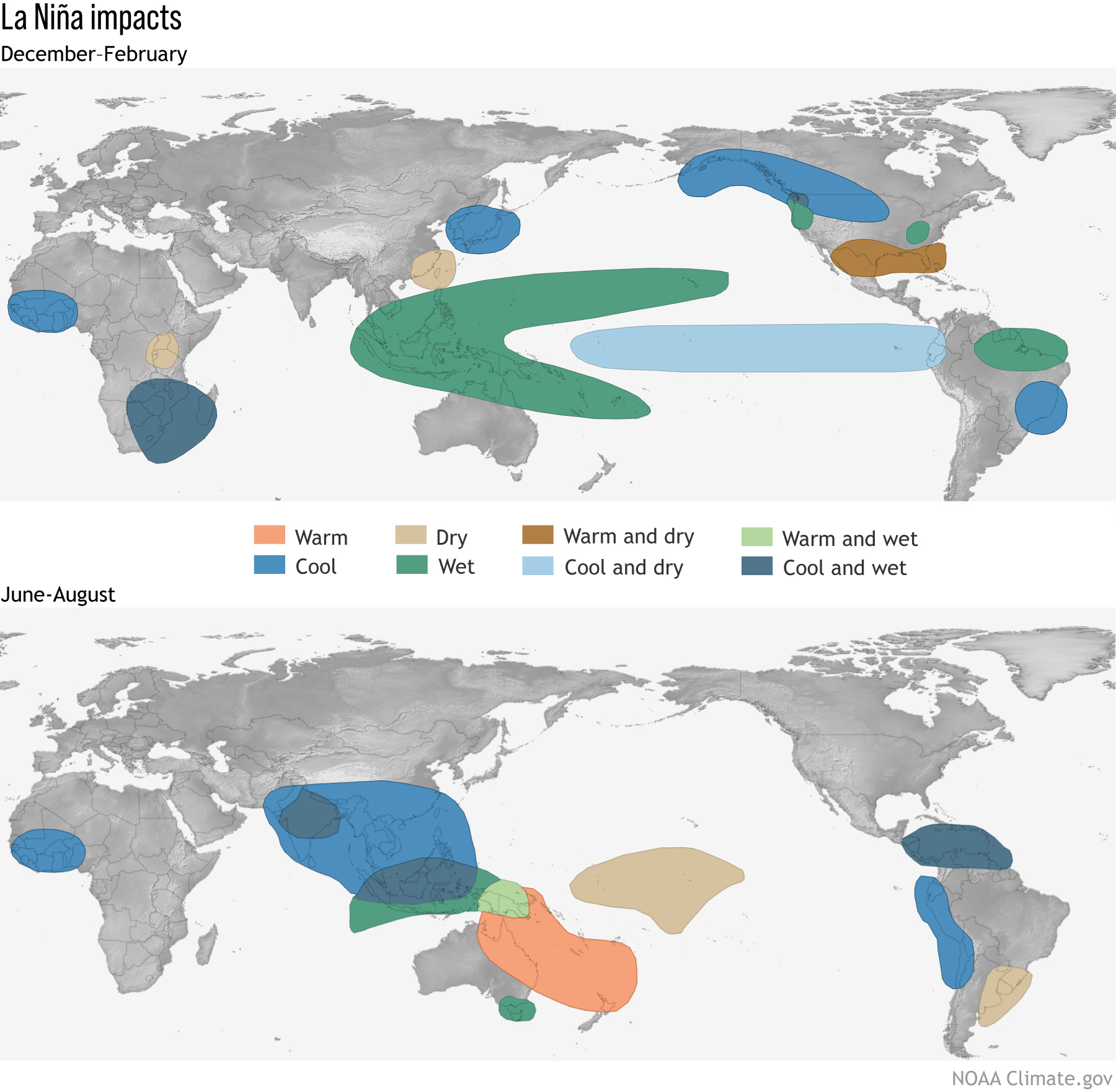
Image: Typical global impacts of La Niña. Source: NOAA/CPC
What is the difference between El Niño and La Niña?
When La Niña is not occurring in the Pacific Ocean, the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is either in a neutral phase of in El Niño.
Neutral ENSO conditions mean that the Pacific Ocean is not having a major influence on the weather or climate in Australia or the rest of the world.
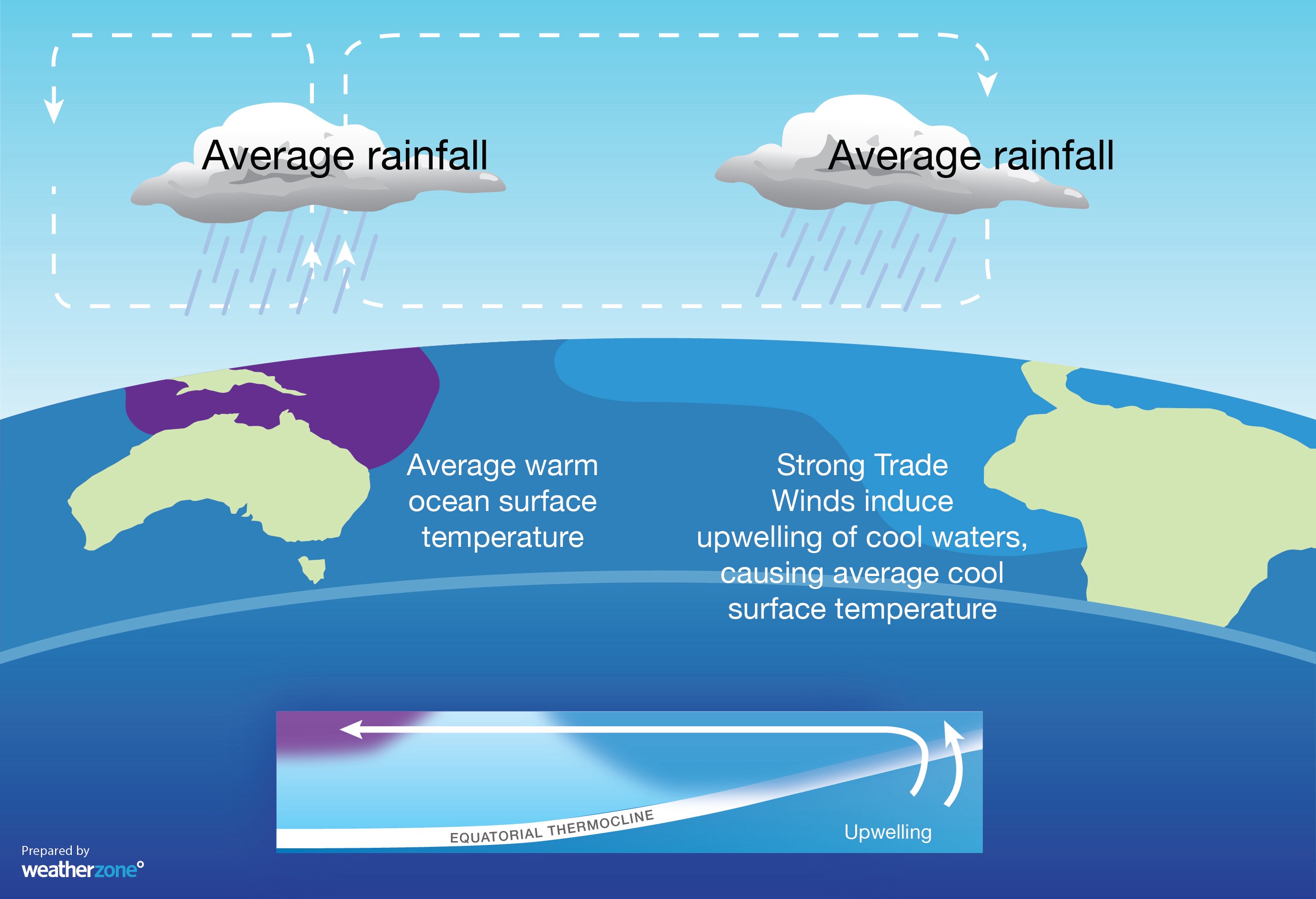
Image: Typical oceanic and atmospheric changes observed during neutral ENSO conditions.
El Niño is opposite to La Niña in its causes and impacts. El Niño is characterised by cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures to the northeast of Australia and abnormally warm water in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean.
The cool oceans and drier atmosphere that are associated with El Niño typically cause decreased convection over the western side of the tropical Pacific Ocean. This in turn drives below average rainfall and cloud cover across much of Australia.

Image: Typical oceanic and atmospheric changes observed during El Niño.
Weatherzone conducts detailed seasonal forecasts which can help with long-term planning out to six months. The seasonal forecasts are tailored to the business and can include risk of heavy rainfall and flood risk, tropical cyclones, thunderstorms, extreme heat, bushfires and much more. These forecasts can be delivered live online or face to face, allowing time for questions and increasing engagement.
For more information on our products or how we can help you with your business needs, please contact us at business@weatherzone.com.au.






